Chitragupta is one such deity, a figure revered as the cosmic recorder, the divine accountant, and the keeper of karma. Believed to meticulously document the deeds of every living being, Chitragupta holds a unique and powerful position in the Hindu pantheon. Through his record-keeping, he upholds the fundamental cosmic law of karma, ensuring justice and balance in the universe.
This blog dives into the origins, symbolism, and spiritual significance of Chitragupta, exploring his role as the god of records and scribes. Whether you’re familiar with Hindu mythology or discovering it for the first time, Chitragupta’s story provides fascinating insights into the themes of morality, justice, and the spiritual philosophy that guides human behavior.
Who Is Chitragupta?
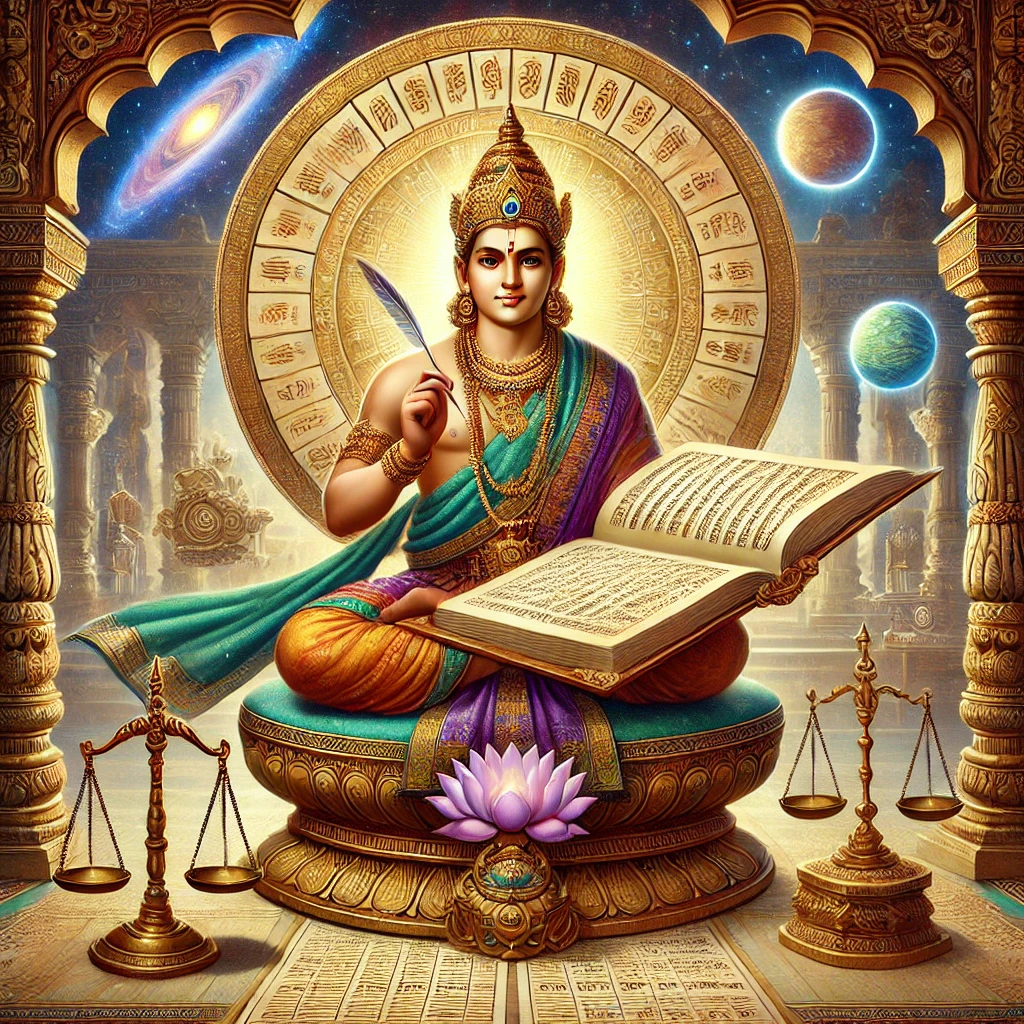
Chitragupta, often depicted with a pen and paper, is seen as the scribe who records every human’s actions throughout their life. As per Hindu tradition, he is believed to serve Yama, the god of death, as a trusted secretary. Chitragupta keeps an accurate account of the deeds—both good and bad—of every soul. According to these records, Yama decides the soul’s fate after death, determining whether they attain heavenly rewards or face the consequences of their misdeeds.
Origins and Mythology of Chitragupta
The origin of Chitragupta traces back to ancient Hindu texts. According to some beliefs, Brahma, the creator god, created Chitragupta from his own mind as a personification of his will to maintain moral order. The Garuda Purana, an ancient Hindu scripture, describes Chitragupta as being born directly from Brahma’s body, endowed with knowledge of the universe, making him an embodiment of divine wisdom and fairness.
Another tale suggests that Chitragupta emerged from Brahma’s inkpot, symbolizing the beginning of written records—a powerful representation of human civilization’s reliance on recording and documenting knowledge.
Why Chitragupta Matters: The Symbolism of the Divine Recorder
The role of Chitragupta goes beyond mere documentation; he symbolizes accountability and moral consciousness. By embodying the act of recording, he emphasizes that every action, thought, and intention matters and will ultimately impact one’s spiritual journey.
In modern terms, one could consider Chitragupta a cosmic “data analyst” who ensures that everyone is accountable for their deeds. This idea resonates strongly in Hinduism, where karma—the law of cause and effect—is a fundamental principle. Through Chitragupta’s records, karma is not an abstract concept but a documented, traceable aspect of one’s life.
The Role of Chitragupta in Hindu Tradition and Worship
Chitragupta’s role as the god of records reflects the importance of truth, integrity, and justice in Hinduism. The reverence for Chitragupta remains evident in festivals and rituals where he is honored, particularly during the Yama Dwitiya festival.
Chitragupta Puja: Honoring the God of Records
Chitragupta Puja, held on the second day after Diwali, is a day dedicated to this deity. Devotees, particularly those in professions involving record-keeping or accounting, offer their respects to Chitragupta. They pray for blessings in maintaining integrity and fairness in their work, as he embodies the principles of honesty and accountability.
The worship rituals include offering ink, paper, and writing instruments to Chitragupta, symbolizing a commitment to truth in documentation. In some regions, people write down their own good deeds and shortcomings, seeking divine forgiveness and hoping to start anew, highlighting the Hindu belief in self-reflection and improvement.
Chitragupta and Yama: Partners in Justice
In Hindu cosmology, Yama, the god of death, is responsible for judging souls and guiding them to their afterlife destination based on their karma. Chitragupta’s role as Yama’s assistant is vital, as he provides the documentation Yama uses to make fair judgments.
This partnership reinforces the value Hinduism places on justice and accountability. It suggests that moral and ethical decisions are guided by an unbiased, well-documented system rather than random chance. Yama and Chitragupta, in essence, serve as protectors of righteousness, reminding devotees that justice prevails in the afterlife.
Chitragupta’s Relevance in Modern Times: Lessons on Accountability and Ethics
Chitragupta’s role as a recorder of karma is as relevant today as ever. In an era where personal accountability and ethical behavior are frequently discussed, the deity’s example serves as a reminder of the importance of maintaining integrity.
The Importance of Recording Our Actions
Just as Chitragupta records deeds to ensure cosmic justice, we can reflect on our own actions and choices. In professional environments, where ethics play a crucial role, adopting Chitragupta’s values can help uphold a culture of transparency and responsibility. His example inspires a proactive approach to accountability, encouraging individuals to consider the impact of their actions on others and the world at large.
Chitragupta as a Symbol of Self-Reflection
Chitragupta’s meticulous recording of every action mirrors the importance of self-reflection. Regularly examining one’s thoughts and deeds can foster personal growth and self-awareness, much like how devotees write their positive and negative actions on Chitragupta Puja. This act of self-reflection aligns with the Hindu philosophy of Atman Dhyanam, or self-knowledge, which is seen as a path to liberation.
Chitragupta and the Ethical Dimensions of Karma
Karma, a principle shared by many Eastern religions, hinges on the belief that every action has a consequence. Through Chitragupta’s role, karma becomes not only a personal journey but also a collective narrative of human conduct. By holding each person accountable for their deeds, Chitragupta upholds moral order and encourages individuals to lead righteous lives.
Balancing Justice and Compassion
One might wonder if karma always deals in strict consequences. Hindu texts reveal a compassionate side of karma, suggesting that sincere repentance can mitigate negative outcomes. Here, Chitragupta’s records play a nuanced role: they allow space for redemption and self-improvement, reflecting the belief that justice does not solely focus on punishment but also on the possibility of growth and positive change.
Chitragupta in Cultural and Artistic Representation
Chitragupta’s role has inspired art, literature, and stories across Hindu culture. In visual representations, he is often depicted sitting with a book or scroll, emphasizing his scholarly nature and the reverence for knowledge. Many Indian temples also feature statues of Chitragupta beside Yama, highlighting their inseparable bond as custodians of justice.
The Pen as a Symbol of Divine Power
One powerful representation of Chitragupta is through his writing instrument, which symbolizes knowledge, wisdom, and the ability to shape destiny. This symbolism emphasizes that while physical strength has its place, it is ultimately wisdom and intellect that define one’s spiritual path.
Embracing the Spirit of Chitragupta Today
Though rooted in ancient mythology, Chitragupta’s message speaks to contemporary values. In a world that often grapples with issues of justice, ethics, and accountability, Chitragupta’s legacy reminds us of the importance of these principles. His role as the god of records invites us to think carefully about our actions, understanding that each choice carries weight in the cosmic ledger of karma.
Chitragupta’s story is not just about a deity keeping records—it’s a call to reflect on our own lives, to strive for truth and justice, and to understand that our actions have far-reaching effects. By honoring Chitragupta, we honor the eternal laws of karma, the significance of moral integrity, and the hope that each individual, through accountability and self-reflection, can work toward a life aligned with the divine principles of justice and righteousness.

Leave feedback about this